Manual Transmission Fluids Explained: Choosing the Right Lubricant for Smooth Shifting and Longevity
In the intricate world of automobiles, every component plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation and longevity. One such often overlooked but vital aspect is the lubricant used in manual transmissions. Just as engines require specific types of oil, manual transmissions demand the right kind of fluid to perform optimally.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nuances of manual transmission fluids, exploring types, properties, and factors that impact performance. Whether you are a seasoned automotive enthusiast or a novice driver, understanding the intricacies of these lubricants will empower you to make informed decisions and enhance the efficiency and lifespan of your vehicle.
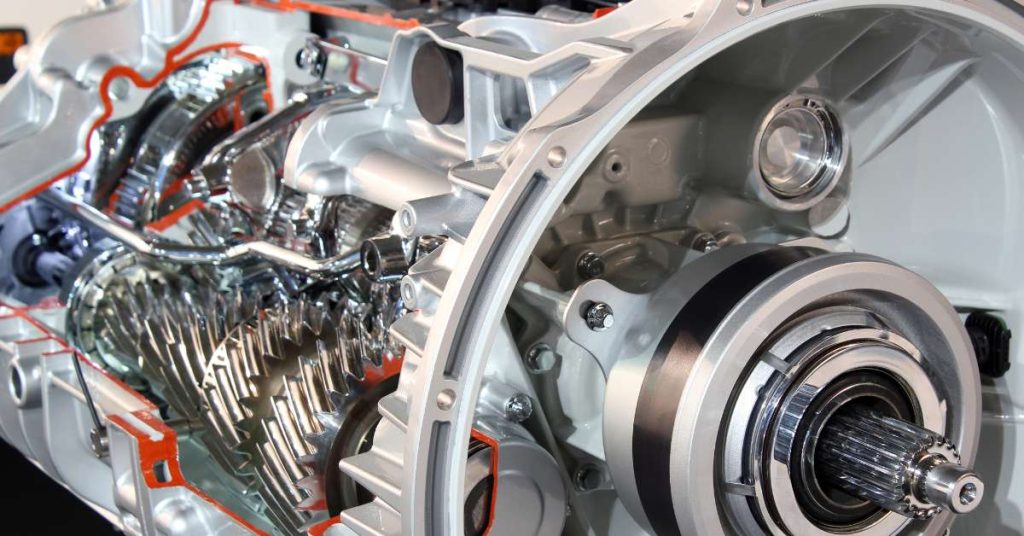
The Basics of Manual Transmission Lubrication
Manual transmissions, unlike their automatic counterparts, rely on the driver to engage and disengage gears manually. This intricate process demands precise coordination between various internal components, and lubrication plays a pivotal role in facilitating smooth gear shifts and preventing wear and tear.
Types of Manual Transmission Fluids
Regular Oils
Conventional mineral-based oils have been the traditional choice for manual transmissions. While they provide adequate lubrication, their performance may degrade over time, especially under extreme conditions. Regular oil changes are crucial to maintaining their effectiveness.
Synthetic Oils
Synthetic transmission fluids, engineered in laboratories, offer superior performance compared to their mineral counterparts. They maintain their viscosity better at high temperatures, resist oxidation, and provide excellent protection against wear and tear. The initial cost may be higher, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the investment.
GL-Rated Fluids
Manual transmissions often require gear oil with specific GL (Gear Lubricant) ratings. These ratings indicate the fluid's ability to withstand the rigors of manual gearbox operation. GL-4 and GL-5 are common classifications, with GL-5 offering enhanced protection but potentially causing issues with certain synchronizers due to its higher levels of additives. Understanding your vehicle's specific GL requirements is crucial.
Key Properties of Transmission Fluids
Understanding the properties of manual transmission fluids is crucial for making an informed choice. Here are the key factors to consider:
Viscosity Grades
Viscosity refers to the fluid's thickness. Transmission fluids are categorized into different viscosity grades, such as 75W-90 or 80W-140. The first number indicates the fluid's performance in cold temperatures, while the second number reflects its behavior at higher temperatures. Choosing the right viscosity grade ensures optimal lubrication in varying conditions, especially in regions with extreme temperature fluctuations.
Additives
Transmission fluids often contain additives to enhance their properties. Anti-wear additives protect metal surfaces from friction, while detergents and dispersants keep the transmission clean by preventing the buildup of sludge and deposits. Some fluids also include corrosion inhibitors to protect against rust, particularly important in areas with high humidity.
Friction Modifiers
These additives play a crucial role in achieving smooth gear shifts. They reduce friction between moving parts, preventing juddering or notchiness during gear changes. High-quality transmission fluids come with carefully balanced friction modifiers to ensure optimal performance without compromising long-term durability.
Tailoring Your Choice to Your Vehicle
Selecting the right manual transmission fluid goes beyond choosing between regular and synthetic oils. Factors such as your vehicle's age, mileage, and drivetrain design should also influence your decision.
1. Vehicle Age:
Newer Vehicles: Modern vehicles often come with advanced engineering and tighter tolerances. Synthetic oils with the appropriate GL rating are usually recommended for enhanced protection and performance.
Older Vehicles: Conventional oils may suffice for older vehicles, but it's crucial to ensure they meet the manufacturer's specifications. In some cases, high-mileage formulations might offer additional benefits for aging transmissions.
2. Mileage:
Low Mileage: Vehicles with low mileage may benefit from synthetic fluids to extend the interval between fluid changes and provide superior protection during operation. High-quality synthetic oils can help mitigate wear during periods of inactivity.
High Mileage: Older vehicles with high mileage might benefit from high-viscosity oils that offer enhanced protection for worn components. Consider fluids specifically designed for high-mileage applications, which often contain additional additives for increased wear protection.
3. Drivetrain Design:
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD): Some FWD vehicles have specific requirements for transmission fluids. Always consult your vehicle's manual or the manufacturer's recommendations. Some modern FWD transmissions may benefit from specialized fluids designed to address unique operating conditions.
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) and All-Wheel Drive (AWD): These drivetrain designs often require different fluids, especially for the rear differential in RWD vehicles. Ensure the chosen fluid meets the specifications for both the transmission and differential. AWD systems may have specific requirements, so it's essential to follow manufacturer recommendations.
The Importance of Routine Maintenance
In addition to choosing the right manual transmission fluid, regular maintenance is paramount for optimal performance and longevity. Follow the manufacturer's recommended fluid change intervals and consider more frequent changes if you subject your vehicle to severe driving conditions, such as towing or extensive stop-and-go traffic.
Routine inspections of the transmission for leaks and proper functioning should also be part of your maintenance regimen.
Ensuring Proper Fluid Levels
Maintaining the correct fluid level is critical for the proper functioning of your manual transmission. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for checking and topping up the fluid. Insufficient fluid levels can lead to increased friction and heat, potentially causing premature wear and damage.
Making an Informed Decision
Now armed with the knowledge of manual transmission fluid types and their critical properties, you can confidently choose the right lubricant for your vehicle. When browsing for options, pay attention to manufacturer recommendations, viscosity grades, and GL ratings.
Regular transmission maintenance, including timely fluid changes, is essential for ensuring the continued smooth operation of your manual transmission.
Conclusion
In the intricate dance of gears within a manual transmission, the choice of lubricant is a choreography that cannot be underestimated. From conventional oils to advanced synthetic fluids, the market offers a myriad of options.
Understanding your vehicle's needs, considering its age, mileage, and drivetrain design, empowers you to make the right choice. By choosing the optimal manual transmission fluid, you not only ensure silky-smooth gear shifts but also contribute to the longevity and overall health of your vehicle.
As you embark on this journey of automotive care, remember that a well-lubricated transmission is a happy transmission.